Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a umbrella term that includes emphysema.
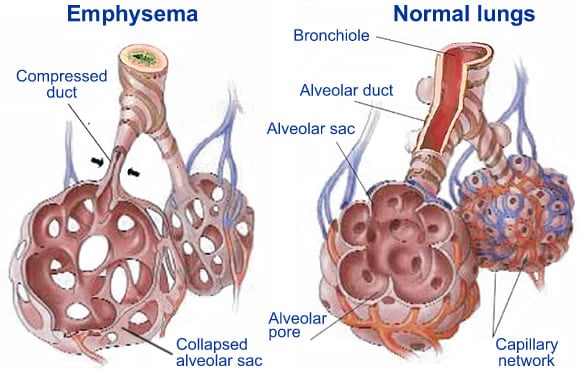
Emphysema is a progressive lung condition that affects the tiny air sacs in the lungs, alveoli, and causes them to fill with air.
Over time these air sacs expand causing them to burst or become damaged, which causes the lungs to form scar tissues.
These scar tissues will begin to affect the patients breathing ability by making them progressively short of breath, which is a side affect known as dyspnea.
Eventually the alveoli turn into swollen air pockets referred to as bullae, eventually causing less and less surface area for the lungs resulting in less oxygen entering into the bloodstream.
When the alveoli becomes damaged so do the tiny fibers that hold open the airways leading to the alveoli, causing them to collapse and trap air every time the patient expels air.
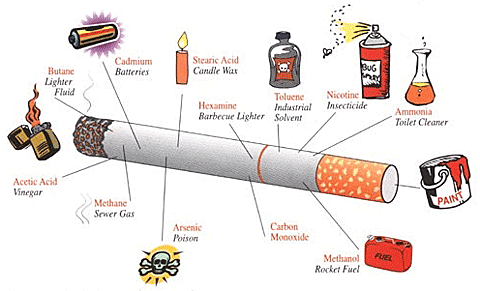
The number one cause of emphysema is long-term cigarette use.