Need help? Call us:
- Questions? Call us toll-free +1-800-520-5726

CPAP Masks Finder
Discover your perfect mask fit
- Portable Oxygen
- Home Oxygen
- Oxygen Accessories
- CPAP Machines
- CPAP Supplies
- CPAP Masks
- Mobility
- Bathroom Safety
- Pediatrics
- New Arrivals
Anti-Inflammatory Foods for COPD Patients
Anti-Inflammatory Foods for COPD Patients

Many of us think of food as fuel that fills our bellies and nourishes our bodies, food can however also help us heal our physical afflictions. Your diet is even more vital to your health and your physical well-being if you are diagnosed with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), most especially if you experience flare-ups every once in a while. This is because the food that you eat can either aggravate or reduce inflammation that comes as a result of COPD.
{{cta(‘155910633031’)}}
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is a normal, yet complex response that cannot easily be reduced to being bad or good. Acute (short-term) inflammation plays an essential role in the protection and healing of the body after you get an infection or a physical injury. When the healing process gets to a certain stage, the immune system shuts itself off and inflammation resolves on its own.
When Inflammation Becomes Dangerous
On the flipside, chronic (prolonged) inflammation can be quite destructive. This occurs when the inflammatory response is out of proportion to the threat it is trying to fight off or when it is directed to the wrong target. The effects can be very disturbing and last for days, months or even years.
Inflammation and COPD
COPD is a respiratory disease characterized by an abnormal inflammatory response in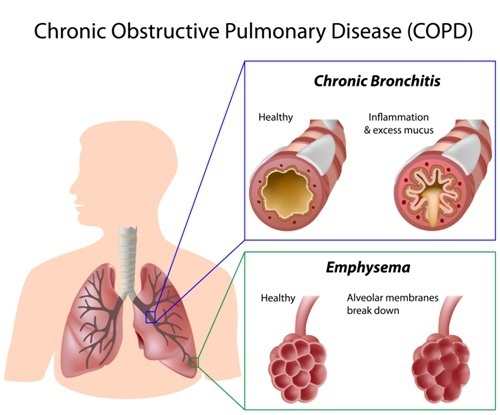 the lungs and restricted airflow, which results in difficulty breathing. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are the two most common conditions that contribute to COPD. The main cause for developing COPD is long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter. Its symptoms include chest tightness, wheezing, a chronic cough, production of a lot of mucus and fatigue. It is the third leading cause of death in the United States.
the lungs and restricted airflow, which results in difficulty breathing. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are the two most common conditions that contribute to COPD. The main cause for developing COPD is long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter. Its symptoms include chest tightness, wheezing, a chronic cough, production of a lot of mucus and fatigue. It is the third leading cause of death in the United States.
How Diet Plays a Role
Anti-inflammatory foods help to reduce chronic inflammation which plays a critical role in the development of many diseases, including COPD. There hasn??t been a lot of research on a diet that can be used as treatment for chronic inflammation, however the research that is available suggests that following an anti-inflammatory diet may help in the reduction of the C-reactive protein. This is a substance in the body found in higher levels when inflammation is present.
Additionally there has been some evidence that anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce inflammation in long-term, inflammation related diseases like metabolic syndrome and diabetes. More research would have to be carried out to substantiate this claim.
You will probably note that anti-inflammatory foods are not that different from eating a healthy regular diet. Below are some foods that help start you off on the right track.
Broccoli
Broccoli is an extremely nutritious vegetable that is rich in sulforaphane, an antioxidant that fights inflammation. It is also a cruciferous vegetable like brussel sprouts or cauliflower. Research shows that eating a lot of cruciferous vegetables is associated with a decreased risk of developing heart disease and cancer. This is believed to be related to the anti-inflammatory effects of the antioxidants they contain.
that fights inflammation. It is also a cruciferous vegetable like brussel sprouts or cauliflower. Research shows that eating a lot of cruciferous vegetables is associated with a decreased risk of developing heart disease and cancer. This is believed to be related to the anti-inflammatory effects of the antioxidants they contain.
Whole Grains
Consuming most of your grains as whole as opposed to refined, can help keep harmful inflammation at bay. This is because whole grains have more fiber, which has been shown to reduce levels of C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation in the blood. Whole grains such as brown rice, bucket wheat, millet, amaranth and quinoa are good for you.
Salmon
Salmon is an excellent source of essential fatty acids and is considered to be one of the best omega-3 foods. Omega-3 fatty acids are some of the most potent ant-inflammatory substances, showing consistent relief from inflammation and reducing the need for anti-inflammatory medication.
Some of the other omega-3 fatty acids sources include sardines, herring and some types of shellfish. Seafood that is either sustainably farmed or wild-caught is the best because the fish has all the nutrients.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are high in Vitamin C, potassium and lycopene, an antioxidant with impressive anti-inflammatory properties. In a review of studies analyzing different forms of lycopene, researchers found that tomatoes and tomato products reduced inflammation more than lycopene supplements. For maximum absorption of lycopene, cook your tomatoes in olive oil.
Dark Leafy Greens
When fighting inflammation, your produce drawer is the first spot that you should fill. Dark leafy greens contain vitamin E which is key in protecting the body against pro-inflammatory molecules called cytokines. If you struggle to eat portions of green leafy vegetables, you can blend them to make a juice. Examples of dark leafy greens that you can introduce to your diet include spinach and kale.
Ginger
Whether used dried, fresh or in supplement or extract form, ginger is an immune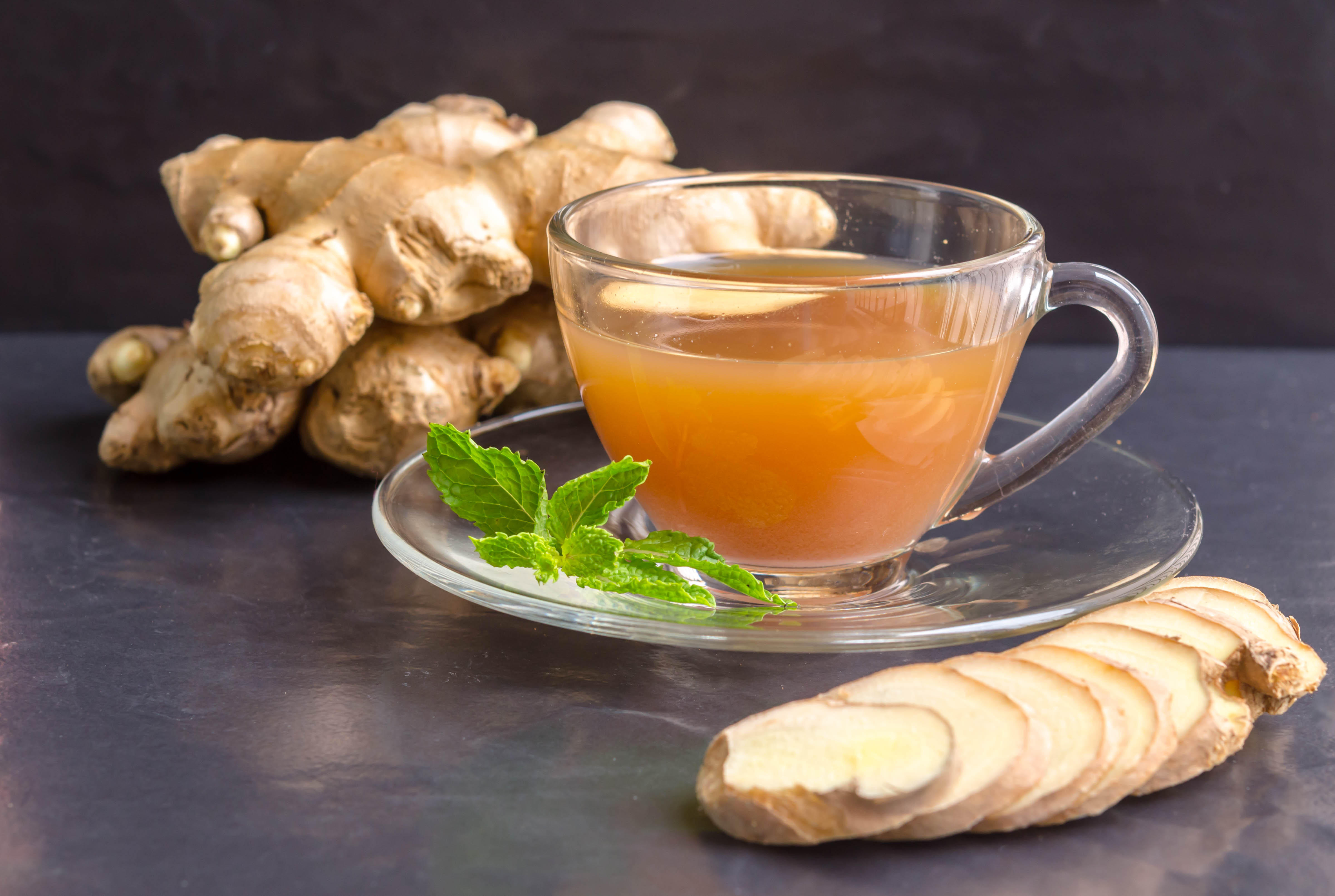 modulator that helps reduce inflammation caused by overactive immune responses. It is also known to clean the lymphatic system. You can take an infusion of ginger or use it as a spice when making meals. If using it in powder form be careful not to inhale it as it may cause irritation.
modulator that helps reduce inflammation caused by overactive immune responses. It is also known to clean the lymphatic system. You can take an infusion of ginger or use it as a spice when making meals. If using it in powder form be careful not to inhale it as it may cause irritation.
Blueberries
Quercetin is a flavonoid found in dark colored berries and helps to fight off inflammation and cancer. One study found that eating a lot of blueberries improved memory and motor function. Scientists in this study believed that this was due to the antioxidants in blueberries protecting the body from oxidative stress and reducing inflammation.
Turmeric
Turmeric??s primary compound, curcumin, is its active anti-inflammatory component. You can use it in recipes or take golden turmeric milk to enjoy its benefits. To increase absorption of its principle, combine it with a pinch of black pepper. Be careful not to inhale this powdered spice as it may cause irritation.
Dark Chocolate
Have a sweet tooth? No problem, you can add dark chocolate to your diet. Dark chocolate is not only delicious, rich and satisfying, but also packed with antioxidants that help to reduce inflammation. Flavanols are responsible for the anti-inflammatory effects in dark chocolate. In order to reap the anti-inflammatory benefits, make sure to choose dark chocolate that contains at least 70% cocoa. A higher percentage would even be better.
Tart Cherries
According to a 2012 presentation by Oregon Health & Science University scientists, tart cherries contain the highest anti-inflammatory content of any food. Research has found that tart cherry juice powder can help athletes recover faster from intense workouts and decrease post-exertion muscle pain. Sweet cherries do not seem to have the same effect, so to yield this benefits, the cherries have got to be tart.
Grapes
Grapes contain anthocyanin which reduce inflammation. They are also a source of resveratrol, a compound that has many other health benefits and decreases the risk of developing several diseases including diabetes, heart disease and eye disorders.
Nuts
Another source of inflammation-fighting healthy fats is nuts. All nuts are packed with  antioxidants which help your body to fight off and repair damage caused by inflammation. Nuts were also part of a study which showed reduction in markers of inflammation in as little as six weeks. Almonds and walnuts have are a good source of this anti-inflammation properties.
antioxidants which help your body to fight off and repair damage caused by inflammation. Nuts were also part of a study which showed reduction in markers of inflammation in as little as six weeks. Almonds and walnuts have are a good source of this anti-inflammation properties.
Green Tea
Green Tea is probably one of the healthiest beverages. It has been shown to reduce the risk of many conditions including Alzheimer??s disease, cancer, heart disease and obesity. Many of its benefits are due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Especially a substance called EGCG which inhibits inflammation by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production and damage to the fatty acids in your cells.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Extra virgin olive oil is one of the healthiest fats that you can eat. Oleocanthol, an antioxidant found in olive oil, has been compared to anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen. In one Mediterranean study, there was a significant reduction in several inflammatory markers in those who consumed 1.7 oz. (50ml) of olive oil daily.
It is important to note that the anti-inflammatory benefits are much greater in extra virgin olive oil than in refined olive oil.
Celery
The benefits of celery include both anti-inflammatory and antioxidant abilities. Celery is also an excellent source of potassium as well as vitamins, and helps to improve blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
{{cta(‘155910633392’)}}
Mediterranean Diet
In addition to lowering inflammation, a more natural, less processed diet can have a great effect on your physical and emotional health, which is quite beneficial for COPD patients who also battle conditions related to this. If you are keen on starting a diet that is closely linked to anti-inflammatory foods, you should talk to your doctor or nutritionist about starting a Mediterranean Diet which is high in healthy oils, nuts, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, fruits and fish.
There are some foods that you should also avoid and these include fatty meats such as lamb or veal, sausages, pork and industrial hamburgers because they are rich in saturated fat and cholesterol, which help in the inflammatory processes of the body. You should also only take low fat dairy and avoid using vegetable oils to reduce the intake of saturated fat and cholesterol.
To help control inflammation, you should also avoid the things that worsen it such as smoking and consuming a lot of alcohol. This will also be good for your overall health as a COPD patient because such habits only make the disease progress faster.































































Comments are closed